Exploring the Wonders of Niacin: The Essential Vitamin B3.
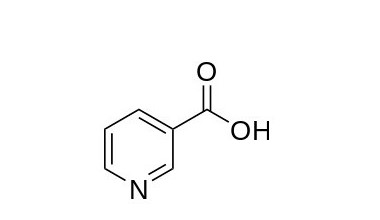
Niacin is the common name of nicotinic acid [ IUPAC: Pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ].
Niacin is a fascinating chemical compound with a plethora of benefits and essential roles within the human body. As a crucial player in the vitamin B family, niacin stands out for its unique features and its importance in maintaining good health.
The Vitamin B3 Family: a trio of vitamers
Vitamin B3 is not a single substance but a collection of three different vitamers: nicotinic acid (niacin), nicotinamide (niacinamide), and nicotinamide riboside. Each of these plays a vital role in our diet and has its own unique functions within the body. However, they share a common destiny: all are converted into Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) once ingested. NAD is a coenzyme found in all living cells and is essential for a myriad of metabolic processes. Without NAD, our cells would not be able to produce the energy necessary for survival, making niacin an indispensable nutrient [1].
Niacin in our diet: Sources and Significance.
Niacin is naturally present in many foods, and its presence is particularly high in fortified packaged foods, meats, poultry, and certain types of fish, such as tuna and salmon. It’s also found in smaller quantities in nuts, legumes, and seeds [2]. The body’s ability to absorb and utilize niacin from these sources is crucial for preventing deficiencies and ensuring that the body’s NAD levels are sufficient for optimal health [3].
The therapeutic power of niacin.
Beyond its role as a dietary nutrient, niacin has therapeutic uses as well. It is commonly used as a supplement to treat pellagra, a condition caused by niacin deficiency. Symptoms of pellagra include skin lesions, gastrointestinal issues, and cognitive disturbances [3]. By supplementing with niacin, these symptoms can be alleviated, showcasing the compound’s vital role in human health.
The Future of Niacin Research.
Research into niacin and its potential health benefits continues to be an active field of study. Scientists are exploring its effects on cardiovascular health, its role in longevity, and its impact on neurological functions. As our understanding of niacin grows, so does our appreciation for this versatile and essential vitamin.
In conclusion, niacin’s importance cannot be overstated. It is a cornerstone of nutrition, a therapeutic agent, and a subject of ongoing scientific inquiry. Its presence in our diet is not just beneficial but necessary for a healthy life. As we continue to uncover the secrets of this remarkable vitamin, we may find even more reasons to ensure it is a staple in our nutritional arsenal.
Syntech International Srl has focused on enhancing the synthesis of niacin via the oxidation of 3-methyl-pyridine with nitric acid. A closed-loop system enabling the complete conversion of NOx back into nitric acid is feasible, making the process entirely viable. A comprehensive description of our study will be detailed in an upcoming post.
References.
[1] Biochemical, Physiological, and Molecular Aspects of Human Nutrition – Elsevier Health Sciences. 4th Edition (2016).
[2] USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference Legacy: Niacin – U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service (2018).
[3] International Journal of Molecular Science 20, 974-1000 (2019).
Author.

Luigi Ambrosi, M.Sc.
Process Chemist – Registered in Italy (BS)
Co-Founder and Chief Scientist at Syntech International Srl
l.ambrosi@syntechinternational.com

